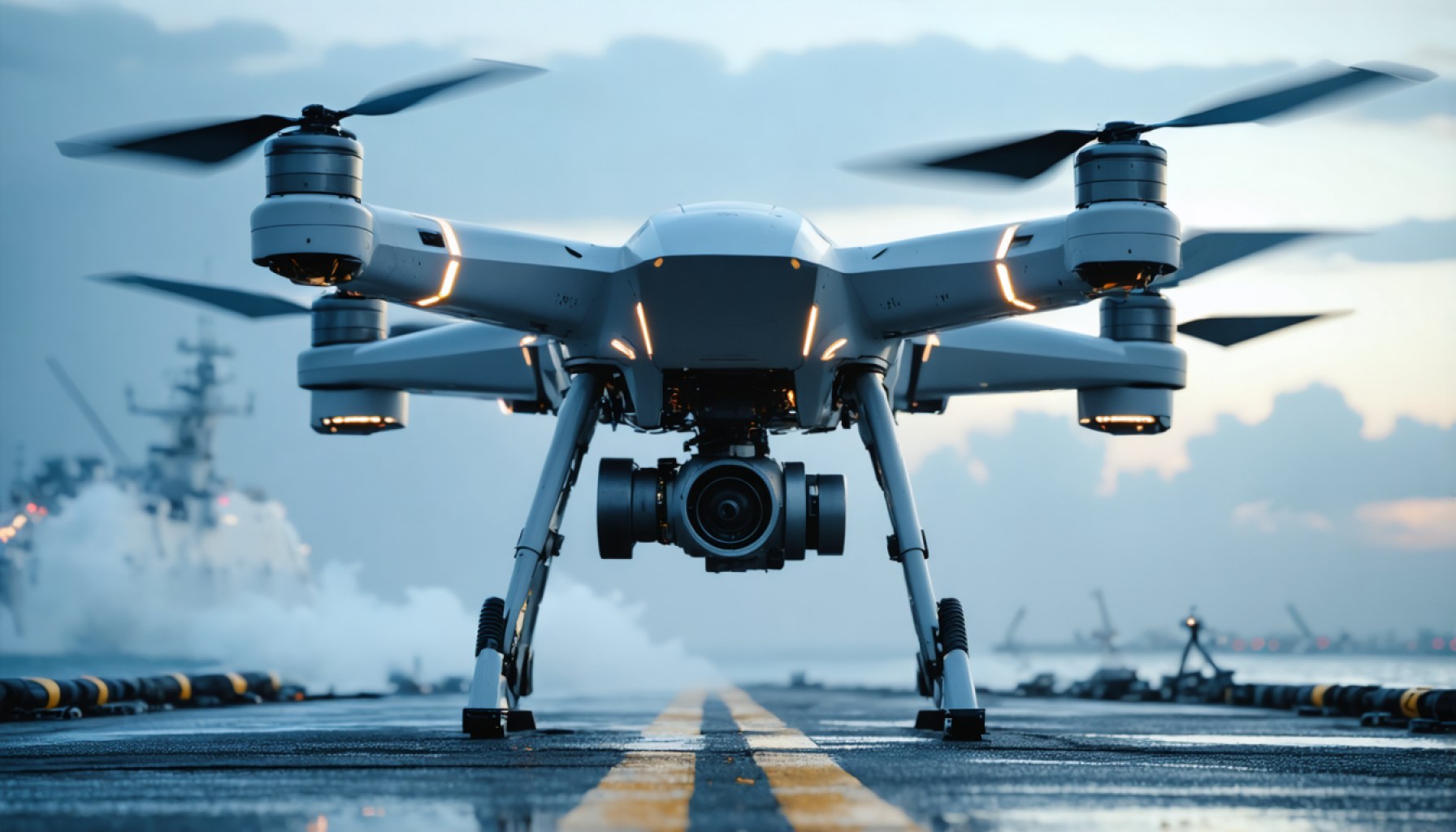
- The U.S. Navy and Air Force are collaborating on Collaborative Combat Aircraft (CCA) drones to fuse manned and unmanned systems in aerial combat.
- The Sea-Air-Space conference highlights the Navy’s plans to enhance interoperability by adopting cross-service standards for drones.
- The MQ-25 Stingray, the Navy’s unmanned tanker, aims to refuel aircraft over 500 miles, showcasing its prowess in carrier operations.
- The integration of the MQ-25 is a crucial step toward mastering drone operations in challenging environments like aircraft carriers.
- The Air Force is developing drone wingmen, such as the YFQ-42, to accompany manned fighters, enhancing tactical capabilities.
- A tri-service agreement between the Navy, Air Force, and Marine Corps fosters technological and strategic collaboration.
- The initiative promises to revolutionize combat aviation with a blend of manned-unmanned systems offering strategic advantages.
Beneath the steel-gray skies of National Harbor, whispers of a technological revolution rise as the U.S. Navy and Air Force synchronize their efforts to redefine aerial combat. As naval leaders exchange insights with their Air Force counterparts, a new era of Collaborative Combat Aircraft (CCA) drones is emerging, promising to blend manned and unmanned systems for optimal battlefield efficacy.
The stage is set at the Sea-Air-Space conference, where Navy officials unveil ambitious plans to infuse interoperability into their ranks by adopting cross-service standards for drone architecture, mission planning, and control. With a vision cast toward a harmonious integration with the Air Force, the Navy envisions a future where their platforms and vehicles are interchangeable, paving the way for a cohesive combat fleet.
Center stage in this unfolding drama is the MQ-25 Stingray, the Navy’s premier unmanned tanker designed to revolutionize operations onboard aircraft carriers. Slated to take flight with the grace of a seasoned performer, the MQ-25 will deftly transfer up to 14,000 pounds of fuel over a daunting 500-mile stretch, all while navigating the challenging theater of highly contested airspace. This initiative isn’t just a leap; it’s a pivotal learning curve for integrating drones into one of the world’s most dynamic operational environments—the aircraft carrier.
Rear Adm. Michael “Buzz” Donnelly, the Navy’s air warfare director, paints a vivid picture of the challenges ahead. The MQ-25 must conquer the high seas, performing complex ballet maneuvers to land on the rolling decks of aircraft carriers, where every moment is a delicate dance against the unpredictabilities of sea and sky. Mastery here is the Navy’s proving ground—a test more rigorous than the drone’s designed combat duties, laying the foundation for an avenue of advance in unmanned aviation.
Synchronizing with the Navy’s timeline is the Air Force’s own CCA initiative, boasting semi-autonomous drone wingmen like the YFQ-42 and YFQ-44. These mechanical sentinels work in tandem with manned fighters such as the F-35 and the forthcoming F-47, enhancing operational depth and tactical advantage. Meanwhile, the Navy watches closely, allowing the Air Force to break new ground before embracing similar technologies in their sea-bound environment.
In a tri-service agreement spanning the Navy, Air Force, and Marine Corps, the collaboration hums along at a productive pace. This alliance is not merely about shared technology but also about exchanging insights and sharing breakthroughs—the knowledge gained is as critical as the hardware developed.
As the MQ-25 readies to conquer its inaugural voyage, the Navy stands on the cusp of a new chapter. This drone, a sentinel of the skies, is more than a link in a logistical chain; it marks the dawn of an era where manned and unmanned elements merge to create an unassailable edge over potential adversaries. In this complex dance of innovation and adaptation, the Navy not only adapts but primes itself to thrive, learning from and contributing to the broader tapestry of military ingenuity.
The future of combat aviation teeters on the edge of the extraordinary, propelled by engineering achievements and strategic foresight. As these drone sentinels prepare to take off into the unknown, they carry not just fuel, but a legacy of excellence and a promise of enduring air dominance.
The Future of Aerial Combat: How Navy and Air Force Drones are Redefining the Battlefield
Introduction
The U.S. Navy and Air Force’s collaboration on Collaborative Combat Aircraft (CCA) drones marks a pivotal shift in modern warfare, setting the stage for unparalleled advancements in aerial combat. These efforts were showcased at the Sea-Air-Space conference, where new strategies were outlined for integrating manned and unmanned systems to achieve superior battlefield synergy.
The MQ-25 Stingray: A Game-Changer for the Navy
Features and Specifications
– Role: Unmanned Aerial Refueling System
– Payload: Capable of transferring up to 14,000 pounds of fuel
– Range: Operates over a 500-mile span
– Capabilities: Designed for high-seas operations, overcoming the challenges of aircraft carrier landings and navigation in contested airspace.
Challenges and Innovations
The MQ-25 will face a rigorous test environment, mastering the complex maneuvers necessary for operations on aircraft carriers. This includes performing under the adverse conditions typical at sea, such as unstable decks and variable weather, which will test and refine its capabilities.
Air Force’s Collaborative Combat Aircraft Initiative
The Air Force’s initiative includes semi-autonomous drones such as the YFQ-42 and YFQ-44, which serve as wingmen for advanced manned fighters like the F-35. This integration:
– Enhances tactical capabilities
– Increases operational depth
– Provides additional strategic advantages leveraging technology
Tri-Service Collaboration
This cooperative dynamic extends to the Marine Corps, forming a tri-service alliance that emphasizes shared learnings and technological advancements across branches. This collaboration ensures that the drones being developed have broad applications and are suited for a variety of missions.
Real-World Use Cases and Predictions
1. Interoperability Milestones: By adopting cross-service standards, the Navy and Air Force aim to create a seamless integration of drones across military branches, potentially leading to unified management systems and mission planning.
2. Strategic Impact: The introduction of drones like the MQ-25 into naval fleets will likely revolutionize logistical support and battlefield operations, providing strategic advantages in refueling and reconnaissance missions.
3. Future Outlook: As technology progresses, these drones could transition from support roles to more tactical roles, providing autonomous decision-making capabilities.
Market Forecast and Industry Trends
The military drone market is expected to see substantial growth over the next decade, driven by advancements in AI, sensor integration, and autonomous technologies. Investments are surging in R&D for drones to perform complex operations independently, underscoring a trend toward increased autonomy and intelligence in military applications.
Pros and Cons Overview
Pros
– Enhanced Efficiency: Unmanned systems reduce the risk to human pilots and can perform missions beyond current limitations.
– Operational Flexibility: Drones extend the reach and capabilities of manned aircraft.
– Cost-Effectiveness: Potentially lower operational costs compared to manned flights.
Cons
– Technical Challenges: Integrating complex systems and ensuring reliability in contested environments requires continuous development.
– Security Risks: Vulnerabilities to cyber threats and electronic warfare need ongoing scrutiny and defenses.
Conclusion and Actionable Recommendations
As the U.S. military branches continue to innovate with CCA drones like the MQ-25, future developments will likely focus on enhancing autonomous capabilities, improving interoperability across branches, and ensuring secure operations. For stakeholders:
– Keep abreast of technological advancements and industry trends.
– Consider investment opportunities in adaptive AI and autonomous systems.
– Engage with cross-industry experts to promote the development of secure and resilient drone technologies.
For more information on military advancements, visit the Navy’s official website or the official Air Force site to stay updated on future developments.