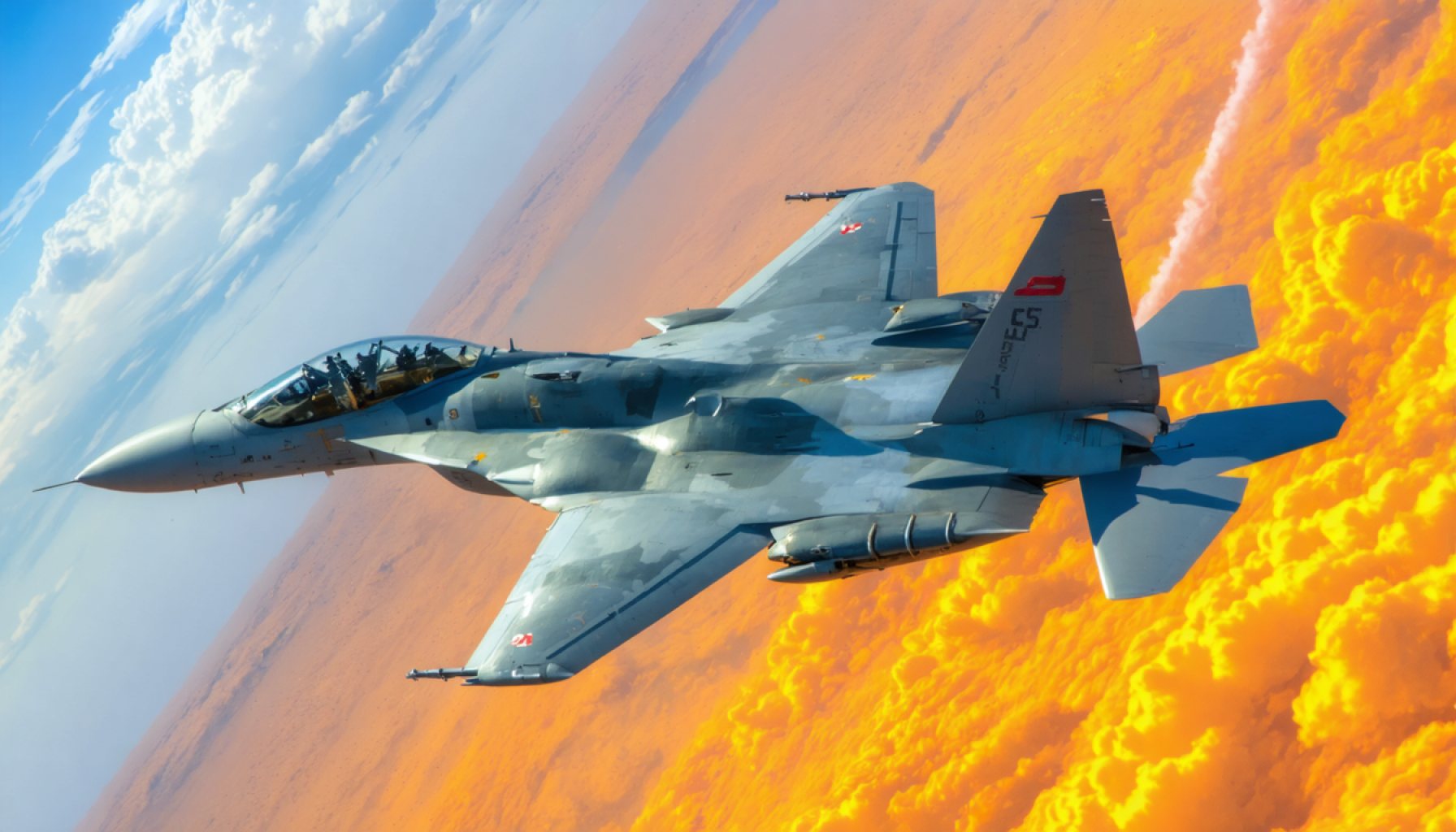
- The Su-35S fighter jets symbolize Russia’s commitment to maintaining a robust aerospace capability amid geopolitical tensions.
- A successor to Soviet-era designs, the Su-35S offers advanced technology and supermaneuverability, highlighted by its Saturn AL-41F1S engines and thrust-vectoring.
- The jets can reach speeds over 1,500 mph and have a radar range of 250 miles, providing tactical advantage in air dominance.
- The Su-35S is versatile, armed with air-to-air and precision-guided munitions, playing a vital role in Russia’s fighter fleet.
- Used by countries like China and Algeria, the Su-35S serves as both a military asset and diplomatic tool.
- Russia faces challenges such as Western sanctions and supply chain issues, necessitating increased production and skilled labor to sustain aerospace goals.
- Questions remain on how the Su-35S will adapt to digital warfare and stealth innovations of modern combat.
Russia’s aerospace ambitions have once again pierced the clouds with the delivery of the Su-35S fighter jets to the country’s Aerospace Forces. Evoking both history and future promise, these newcomers aren’t just aircraft—they’re a symbol of Moscow’s unwavering resolve to stand tall on the global stage despite mounting geopolitical tensions.
Emerging as an evolved giant from its Soviet-era predecessor, the Su-35S is a product of Sukhoi’s innovation, a reputable titan in military aviation. These fighter jets, labeled generation 4++ fighters, encapsulate a blend of lethal maneuverability and sophisticated technology. Picture thunderous Saturn AL-41F1S engines, wreathed in a roar of power, propelling this beast to supermaneuverability. The thrust-vectoring capabilities empower the Su-35S to dance through the skies with acrobatic finesse, unmatched by many of its contemporaries.
Capable of cruising over 1,500 miles per hour and traversing vast distances without the need for refueling, this aircraft stands as a testament to tactical and strategic versatility. Its radar, the Irbis-E array, acts as a sentinel, probing the skies for targets up to 250 miles away, handing pilots a critical vantage in maintaining air dominance.
The Su-35S isn’t merely a machine of war—it’s an ecosystem of adaptability. Armed with an arsenal ranging from air-to-air missiles like the R-77 to precision-guided munitions for ground targets, it solidifies its critical role within the Russian fighter fleet, serving as a workhorse against both aerial threats and ground confrontations.
An era of modernity juxtaposed with tradition, the Su-35S battles not just in skies but in the geopolitical arenas. With other nations, like China and Algeria, integrating these jets into their forces, the Su-35S emerges as a diplomatic lever as well—an affordable alternative to Western offerings that comes unburdened by alliance strings.
Yet, the skies aren’t entirely clear for this warbird. Russia’s on-going challenges, from Western sanctions to supply chain strains, require a deft balancing act. Increasing production rates, as emphasized by UAC’s leadership, is not just about meeting current demands but safeguarding future aspirations. This effort is underscored by the need to attract skilled workers and ramp up local capabilities to circumvent international barriers.
As the world holds its breath, wondering about the balance of power, the Su-35S jets are more than Russia’s statement of strength—they’re a strategic play. In a landscape where air superiority often dictates terms, these aircraft are paving the way for what lies ahead. For Russia, supporting its Aerospace Forces with cutting-edge fighters like the Su-35S is not merely a necessity—it is a testament to resilience against headwinds of change.
In the end, the question looms: Can the Su-35S claim its space amidst evolving digital warfare and stealth-centric arenas? Only time will reveal if these formidable machines can navigate the shifting currents of modern warfare, ensuring that the Russian skies remain vigilantly guarded.
The Su-35S: Russia’s Next-Gen Fighter Jet That Challenges Global Air Dominance
Introduction
Russia’s recent delivery of the Su-35S fighter jets to its Aerospace Forces underscores a renewed ambition in military aviation. Emerging from the legacy of Soviet-era engineering, the Su-35S symbolizes Russia’s strategic resolve to assert itself amid global tensions. This article delves deeper into the intricate details of the Su-35S, its capabilities, and its geopolitical impact, while addressing pressing reader questions and offering actionable insights.
Features, Specs, & Pricing
The Su-35S is a 4++ generation fighter jet, positioned just below fifth-generation aircraft in terms of capabilities. Key features include:
– Thrust-vectoring engines: Equipped with Saturn AL-41F1S engines, the jet offers supermaneuverability, allowing for nimble airborne acrobatics.
– Speed: It can reach over 1,500 miles per hour, making it one of the fastest jets in the skies.
– Range & Endurance: Capable of long-range operations without refueling, thanks to its impressive fuel capacity and efficient design.
– Radar System: The Irbis-E radar monitors up to 250 miles, providing superior situational awareness and target acquisition.
– Armament: Features an arsenal of weapons, including R-77 air-to-air missiles and precision-guided munitions.
Pricing for the Su-35S is estimated to be significantly lower than comparable Western fighters, contributing to its appeal in international markets.
Geopolitical Role & Market Trends
The Su-35S is not only a military asset but also a diplomatic tool. Nations like China and Algeria have already integrated these jets, enhancing their defense capabilities without the political strings associated with Western military hardware. This trend suggests a broader market potential, especially among countries seeking reliable and cost-effective alternatives to Western offerings.
Comparisons & Controversies
While the Su-35S boasts impressive specifications, it faces competition from Western fighter jets like the F-35 Lightning II and the Eurofighter Typhoon. Critics point out that, despite its capabilities, the Su-35S lacks the stealth features of fifth-generation competitors. However, its affordability and agility remain strong selling points.
Challenges & Limitations
Western sanctions and supply chain issues pose challenges to production and development. Russia is focusing on increasing local production capabilities and attracting skilled personnel to mitigate these issues. Additionally, the evolution of digital warfare demands ongoing upgrades to electronic warfare suites and cybersecurity measures.
Security & Sustainability
While the Su-35S bolsters Russia’s defense posture, its long-term sustainability will depend on innovations in next-generation technologies, reduction of emissions, and continued enhancement of electronic warfare capabilities to deal with stealth-centric threats.
Pressing Questions & Recommendations
– Can the Su-35S compete in stealth-centric warfare? While it lacks full stealth capabilities, its advanced radar and maneuverability offer compensatory advantages. Continuous upgrades and innovations will be crucial.
– What are the strategic advantages for Russia? The Su-35S enhances Russia’s air superiority and provides a versatile platform for both defense and diplomatic leverage.
Quick Tips for Industry Observers
1. Monitor emerging markets: Watch countries with rising defense budgets for potential Su-35S sales.
2. Evaluate tech advancements: Keep an eye on Russia’s investment in stealth and electronic warfare technology as these will impact the Su-35S’s future performance.
3. Stay informed on geopolitical shifts: Changes in alliances and regional tensions may influence Su-35S deployment and international sales.
For more detailed information, visit United Aircraft Corporation.
Conclusion
As Russia positions the Su-35S in the competitive landscape of modern warfare, its future will hinge on technological adaptability, market dynamics, and geopolitical strategy. While it faces challenges, the Su-35S remains a potent tool in Russia’s aerospace ambitions—and a pivotal player on the global stage.